

Infectious diseases are one of the most common diseases that patients seek medical treatment for. The main reason is that pathogens (bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc.) attack all parts of human body, causing inflammation, headache, fever and other symptoms. The top priority for treating infectious diseases is to find out the pathogens and prescribe targeted drugs, so as to cure them in a better and faster way. Therefore, to find out pathogens early, rapidly and accurately is of great significance for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis.
A series of research findings were published
In October 2022, the team led by Professor Gu Bing of our hospital, together with the team led by Professor Wang Shengqi of the Research Academy of Military Medicine, developed a new technique for multi-target, rapid, highly-sensitive and accurate detection of pathogens for early diagnosis of infectious diseases on the basis of membrane-like signal labels. The relevant research findings have been recognized by international peers. They published papers titled “Introduction of graphene oxide-supported multilayer-quantum dots nanofilm into multiplex lateral flow immunoassay: A rapid and ultrasensitive point-of-care testing technique for multiple respiratory viruses (multiple immunochromatography assay with graphene oxide multilayer quantum dot film as carrier: A rapid and ultrasensitive POCT technique for multiple respiratory viruses)” and “Ultrasensitive and multiplex detection of four pathogenic bacteria on a bi-channel lateral flow immunoassay strip with three-dimensional membrane-like SERS nanosticker (immunochromatography assay based on three-dimensional membrane-like SERS molecular markers, highly-sensitive and multiplex detection of four pathogenic bacteria)” in the “Nano Research”(Excellence Action Plan-Leading Journal, CAS, Q1,IF= 10.269) and the“Biosensors and Bioelectronics”(CAS, Q1, F=12.545) respectively.
A flexible membrane-like nanoprobe has been developed innovatively
The team members have developed a high-performance flexible membrane-like nanoprobe with single-layer graphene oxide film as the carrier. In addition, they have developed highly-sensitive immunochromatographic detection reagents for joint detection of respiratory pathogens and common pathogenic bacteria respectively by introducing highly-sensitive quantum dot fluorescent labels and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) molecular markers.
Compared with conventional spherical nanomaterials, the flexible membrane-like nanoprobe has a larger relative surface area, higher antibody load and stronger optical signal. It can quickly wrap the surface of a target pathogen to improve the fluidity and stability of the pathogen/probe compound on the test strip and significantly improve the sensitivity and detection throughput of conventional technology.
The detection sensitivity has been increased by 100 times
The team found that using a membrane-like multilayer quantum dot probe to construct a three-channel immunochromatography assay test strip for detecting SARS-CoV-2, influenza A virus and adenovirus simultaneously can achieve detection limits of 8 pg/mL, 488 copies/mL and 471 copies/mL respectively, and detection time of less than 15 minutes. The sensitivity of the method is about 100 times higher than that of conventional colloidal gold strips and 12 times higher than that of commercial ELISA kits. In addition, the multi-channel test strip has shown excellent performance in real respiratory tract specimen addition experiments and multiple SARS-CoV-2 variant detections, with the potential to be developed as a highly-sensitive on-site detection reagent.
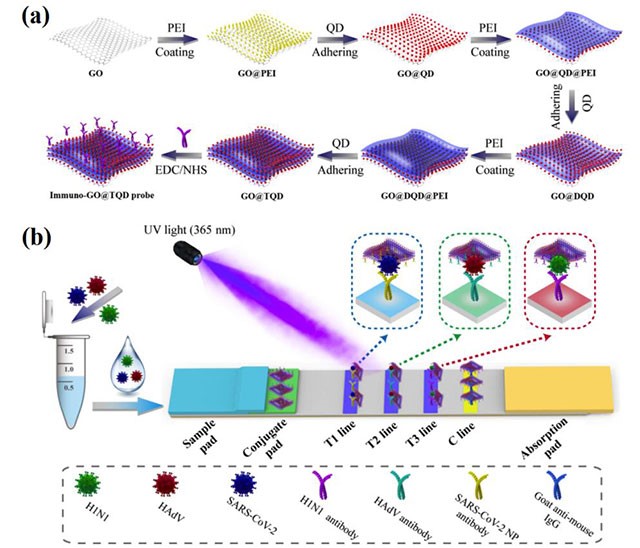
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram of the Preparation Process of Membrane-like Multilayer Quantum Dot Fluorescent Label and of Quantitative Detection of Three Respiratory Viruses
The team also developed a highly-sensitive immunochromatography assay technique for bacteria detection by using a multi-hotspot membrane-like SERS probe. The technique can simultaneously, quickly and accurately identify 4 important pathogens in complex clinical samples and environmental samples, with a sensitivity of 10 cells/mL (500 times higher than conventional colloidal gold test strips), and a total detection time of less than 20 minutes.
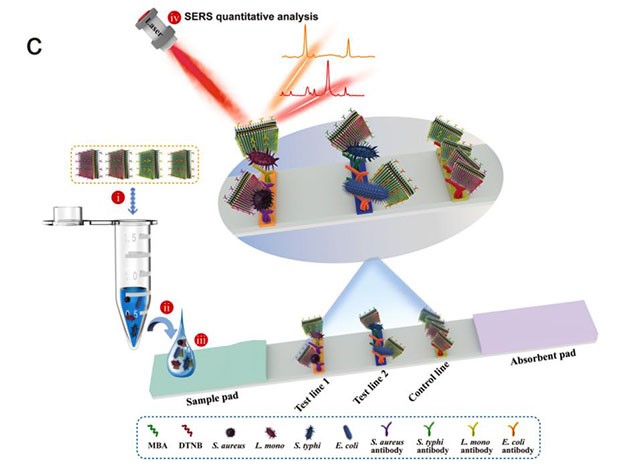
Figure 2 Schematic Diagram of Detection of Four Bacteria Based on SERS-LFA
Significance and value
The POCT respiratory virus triple detection technique has targeted mainly at epidemic disease viruses in recent years. It can identify novel coronavirus, influenza A virus and adenovirus in a highly-sensitive and rapid way and can be used for screening and treatment monitoring in multiple sites including hospitals, communities, customs and homes, which is of strategic significance for the control of spreading of respiratory viruses and the containment of COVID-19 in China. The POCT pathogenic bacteria quadruple detection technique targets at pathogens of clinical attention, including Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli. The technique has expansibility in detention of pathogenic bacteria and can directly diagnose pathogenic bacteria for clinical samples. It is expected to shorten the identification time of infectious diseases, improve diagnosis efficiency, provide accurate treatment basis and reduce both disease and medical burden.
Introduction to team members
Wang Chongwen, Associate Professor, Master Tutor of School of Life Sciences, Anhui Agricultural University, Postdoctor of Research Academy of Military Medicine, Academy of Military Sciences, part-time Master Tutor of School of Laboratory Technology, Xuzhou Medical University, is mainly engaged in the research on new molecular diagnosis techniques, new biological sensing techniques, rapid detection of pathogenic microorganisms and other fields. He has won the first prize of Military Science and Technology Advance Award (7/14) in 2016, the first prize of Academician Zhuang Hui Award Fund, and applied for 13 national invention patents. The diagnostic kit for IgM/IgG antibody to new coronavirus (quantum dot method) developed by him urgently in 2020 has won national medical device certificate (No.: Guo Jie Zhu Zhun 20203400536) and military specific drug approval (No.: Jun Yao Zhu Zi Q2020002). As the first author (at the top place)/corresponding author, he has published more than 40 papers (including 28 papers in CAS Q1, 11 papers with IF>10) in well-known SCI journals and 4 papers were selected as highly cited papers according to ESI. He is also a member of the Biomarker Committee of Chinese Research Hospital Association, the Chinese Society of Laboratory Medicine of China Association of Medical Equipment, and the POCT Branch of China Association for Medical Devices Industry.
Gu Bing, MD, Professor, Ph. D Tutor, Director and Academic Leader of the Laboratory Department of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, is a visiting scholar of Purdue University and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), a key medical talent under the provincial “Science and Education-based Health Strengthening Project" and a high-level health talent under the "333 Project" “Six-Field High-level Talent Cultivation Project” and "Six One Project". He is Vice Chairman of the Youth Committee of the Laboratory Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Vice President of the Laboratory Medicine Branch of China Association of Medical Equipment, Director of the Guangdong Clinical Genetic Testing Quality Control Center, and President of the Laboratory Economics Branch of Health Economics Association of Guangdong Province. He is engaged in research of new techniques for the rapid detection of major infectious diseases as well as the prevention and control of infection of drug-resistant bacteria. He has been in charge of 5 national natural science funds and 8 provincial and ministerial research projects, and published 106 SCI papers as the first author or corresponding author, with cumulative IF=562 and H-index=34. The papers have been cited more than 4,700 times. He has participated in 18 academic monographs as a chief editor or associate editor and won 7 patents and 8 technical awards.
Wang Shengqi, Researcher and Ph. D Tutor of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Director of the National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Nucleic Acid Drugs, Deputy Director of the National Engineering Research Center for Biochips, and Director of the Key Laboratory for New Molecular Diagnosis Techniques of the PLA and Beijing Infectious Diseases. He is mainly engaged in the research on molecular diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. He has ever won National Outstanding Youth Fund, “Truth Seeking” Outstanding Youth Award and Wu Jieping Medicine Innovation Award and is among the first batch of talent under the “National New Era Ten Million Talent Cultivation Project”. He has won 1 second prize of National Technological Invention Award, 1 second prize of National Scientific and Technological Advance Award and 4 provincial and ministerial first prizes as the first person of accomplishment and has been authorized 23 invention patents. In addition, he has won 65 national or military registration certificates for testing products he developed and published more than 160 SCI papers.
Text: Zhao Yunhu, Wang ChongwenPhoto: Zhao Yunhu